Hot rolled steel or cold rolled steel – which to choose? One of the crucial parts of an engineer’s job is picking the right materials for their application. There’s already a lot of types of metal to choose from. Each with its own
advantages and uses. Some types of steel make an excellent fit for home appliances, others for the automotive or marine industry, gas tanks, constructions, etc. Still, there’s one more distinction to make. A material grade with the same chemical composition may have varying qualities depending on the manufacturing method.
Hot Rolled Steel
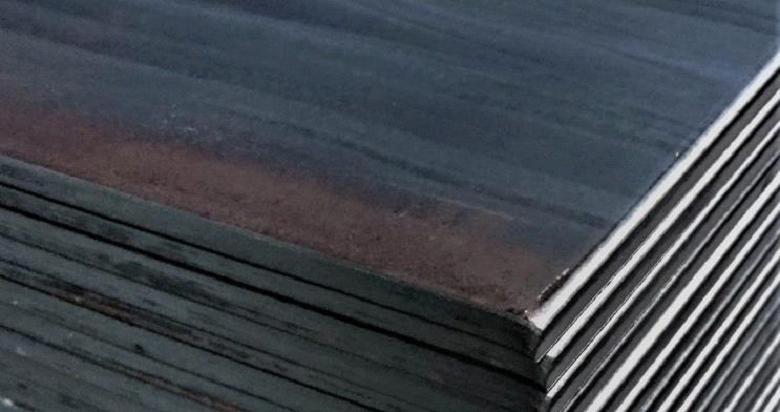

Hot working is more widely used compared to cold working because it needs less force and energy. It is used in compressive forming methods like rolling, extrusion, forging, etc.
Hot Rolling Method
Hot rolling takes place in temperatures above the material’s recrystallisation temperature. In case of steel, the temperatures rise above 1000°C.

The starting material is usually steel billets or slabs. First, they are heated above the aforementioned temperature. The next step is feeding them to the rolling machinery. Continuous rolling gives the desired final shape – a metal sheet (3 mm and upwards) or profile.
Hot Rolled Steel Properties
As it is easy to form metal in high temperatures without any extra delays, it is possible to produce it in larger quantities than cold rolled steel. This keeps the market price of hot rolled steel lower. The steel cools at room
temperature. This is known as normalising. It changes the material’s microstructure in a way that results in increased ductility and toughness. Ductility is especially important when forming the material (e.g sheet metal
bending) to give it the required shape for your needs. Hot rolled steel, though, doesn’t have the best quality. It shrinks slightly during the cooling process. This leaves the metal with internal stresses. The results are nonuniform measurements and some distortions. The material’s dimensional tolerances can vary between 2…5%. Also, the surface has a scaly finish. This is a kind of oxide that forms at high temperatures, known as mill scale.
It is easy to identify hot rolled products by touching the surface because of the uneven finish but it is also lacking an oily film. With steel bars, the corners are rounded.
Hot Rolled Steel Uses

Hot rolled steel is a good choice when tight tolerances are not of utmost importance. There are many fields where that is the case. Its great advantage in price matters more than precision. Some common uses for
hot rolled steel are:
Constructions
Pipes and tubes
Truck frames
Doors and shelving
Railroad tracks
Railroad car parts
Cold Rolled Steel
Cold working is a metal forming method that has many advantages over hot working. Technically, cold working includes cold rolling and cold drawing. The former is a process used with sheet metal. The latter finds use with
rectangular and round bars.
Cold Rolling Method
As opposed to hot rolling, cold rolling occurs with the metal below its temperature of recrystallisation. This is still only half the truth. The whole process starts out like hot rolling to give the initial shape without much
resistance. After that, the metal is left to cool at room temperature.
The half-products are then fed to cold reduction mills. The metal is rolled to the thickness of 0.5…3 mm in case of mild steel and 0.5…5 mm in case of stainless steel.
The material is cooled by the use of oil which also acts as a lubricant during the rolling process. As the metal sheet gets thinner between the rolls, its speed increases. That would mean material wear and deformation if an oil film wasn’t there to minimise the contact. Therefore, cold rolled steel is identifiable by an oily and smooth surface.
As the working takes place in temperatures below the rescrystallisation temperature, strain hardening occurs. The rolls induce plastic deformation. Thus, the yield strength of cold rolled steel is higher than that of hot
rolled steel. As an example, a hot rolled steel product may have a yield strength of 235 MPa. In comparison, a cold rolled steel product with the same chemical composition has a yield strength of 365 MPa.
The main advantages of cold working are
Accurate finished dimensions
Clean surface
Greater strength properties
Cold Rolled Steel Uses
Although cold rolled steel is more expensive than hot rolled steel, the aforementioned advantages make it useful for many applications. The finished products need less additional surface finishing to achieve a good
result, as the surfaces are already smooth. Examples of cold rolled/cold drawn steel uses include
Metal furniture
Structural parts
Home appliances
Water heaters
Metal containers
Fan blades
Frying pans
Computer cabinets
When choosing the right material for your product, make sure to understand the difference of these two material manufacturing methods. There is no point in spending more money on something you don’t actually need.
Therefore, hot rolled steel is the better choice when the demands aren’t high. Otherwise, go with cold rolled steel. It has the answers that hot rolled steel doesn’t.



 فارسی
فارسی